Quality and Test Systems
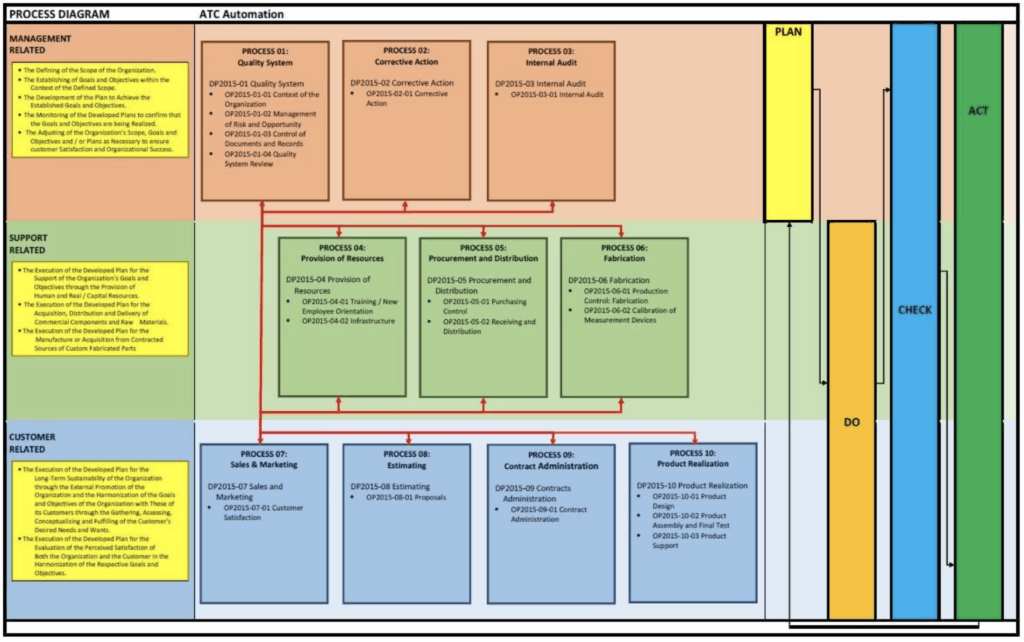
The process to ensure Quality at ATC falls into two categories: a) QMS (Quality Management System) for governing our business practices, and b) Quality Design Methodology to ensure World-Class statistical compliance of product produced by our equipment.
Quality Management System
QMS: The first part of Quality concerns QMS procedures, are established in the ATC Quality Manual in compliance with ISO 9001-2015 and audited bi-annually. The Quality Manual gives a high level overview of ATC’s management system with each level of subsequent documentation providing more detail. Further guidance is provided with our Process Definition Documents, the Operating Procedure Documents, and the Work Instruction documents.
The Process Definitions describe ATC Automation’s key processes (including a representative process flow diagram) and references the associated Operating Procedures. The Operating Procedures describe the control measures implemented to ensure each process achieves the expected results. The Work Instructions describe the step-by-step actions to be taken to successfully execute the control measures listed in the Operating Procedures.
Quality Design Methodology
QDM: The second part of Quality is defined by Quality Design Methodology and procedures employed by ATC Automation during the design and execution of capital equipment projects. These vary widely by both customer direction and end-user requirements. Quality begins with adherence to proven design philosophies and methods to achieve the assembly or test goals, and typically includes preparation of a PFMEA and DFMEA with customer involvement. It must also include lessons-learned from previous, similar design aspects, and the customers’ product knowledge.
Depending on customer directives, QDM is implemented in a variety of ways. It can range from simple process-verification by way of discrete sensors and smart sensors, but can also include technologies ranging from machine vision inspection, 2D and 3D laser scanning/mapping, and performance testing. QDM typically includes in-process verifications such as fastener torque control and monitoring, assembly press force control and monitoring, and component assembly verification within dimensional limits. It can utilize vision mapping and control to drive operations such as robot-manipulated part handling, material dispensing, and part assembly to ensure a conforming process.
Performance testing to verify product quality and functionality can include many different technologies, ranging from leak or flow testing, simple electrical testing, electronic testing, actuation of the product/verification of operation, etc. High-speed data capture is often employed to monitor product device signals and correlate to established max/min thresholds established by the end-user. Testing can also include measurement of forces applied to and by actuated components, electrical measurements of said actuated components, noise and vibration analysis, etc. In almost all applications, Performance Testing is defined by the customer and product specifications.
Data extracted from QDM devices is oftentimes compiled and logged to line-side or customer MES systems and tracked against unique identifiers of the product (2D serial codes). This data along with inspection of assembled products in a production sampling is normally performed to verify machine Cmk and process Cpk. Results of these inspections ensure quality product over time. Live data collection and logging to one or more software suites allows for SPC directed control of upstream processes that affect product quality. Utilizing both QMS and QDM, ATC Automation ensures quality for our customers.